|
Enantiomer ( Chiral ) Separation Columns
/ Protein Ligand Columns
Cation Exchange Columns / Gas Chromatography Columns
-
Enantiomer ( Chiral ) Separation Columns
-
Enantiomer ( Chiral ) Separation Example Chromatograms
-
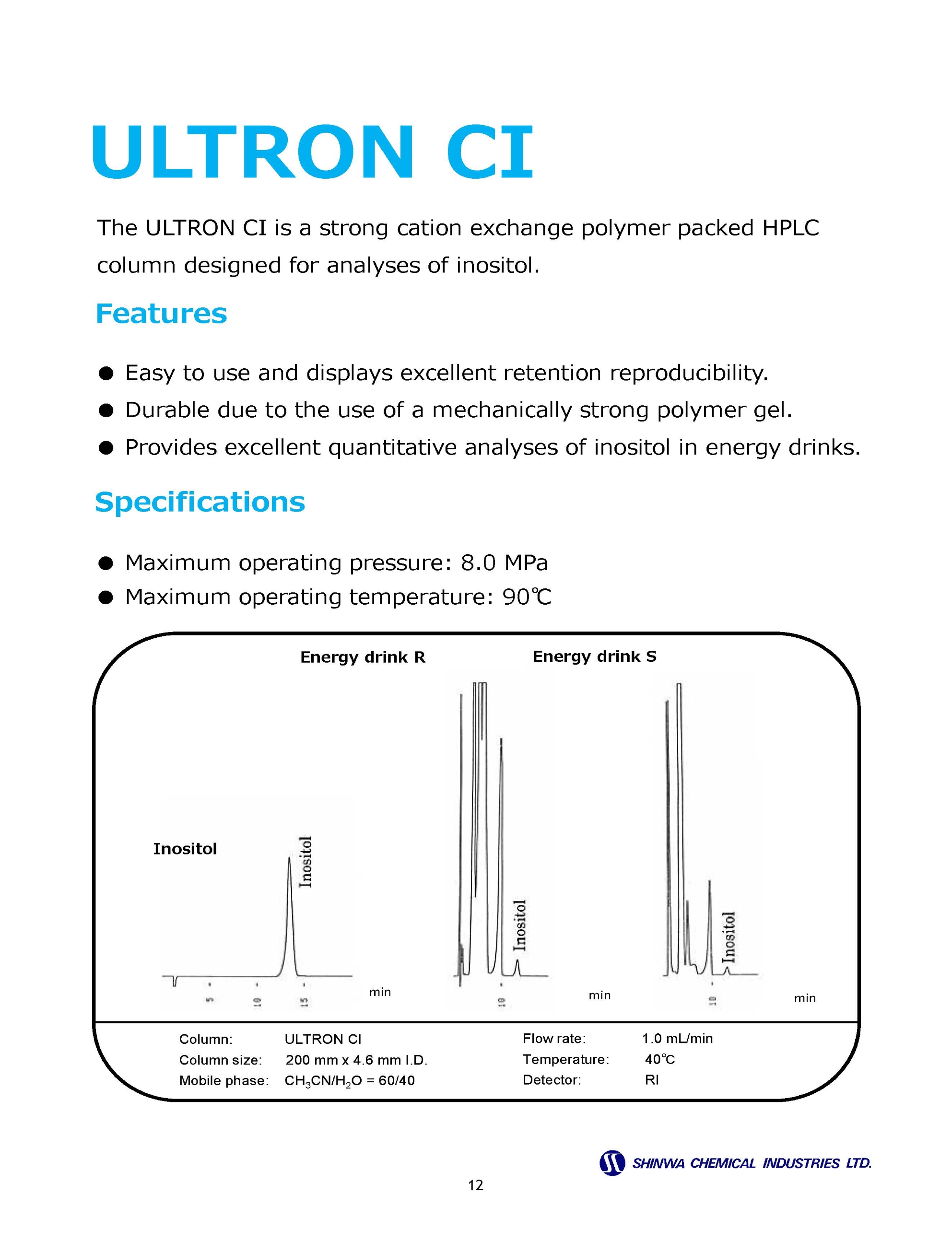
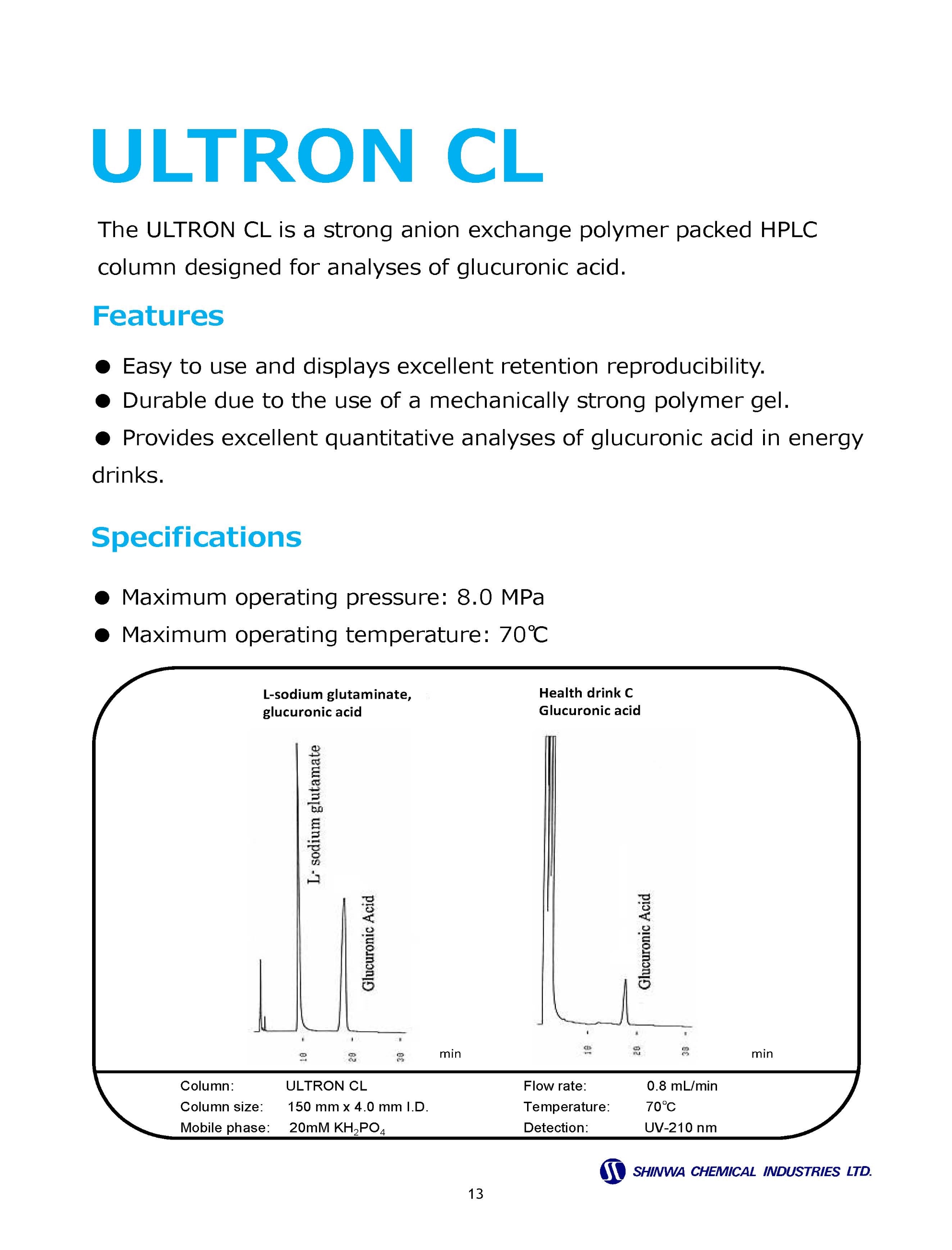
Cation Exchange Columns
-
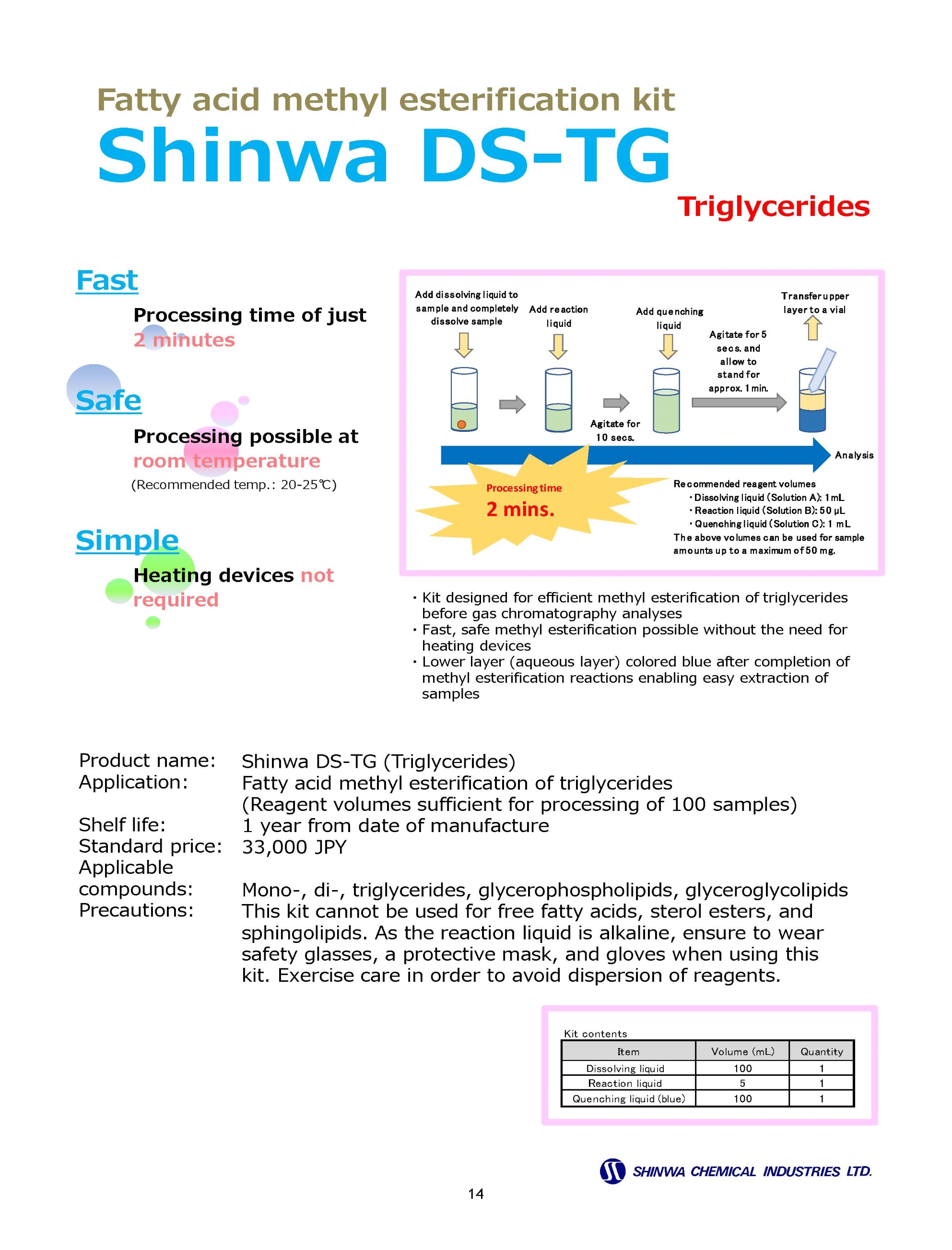
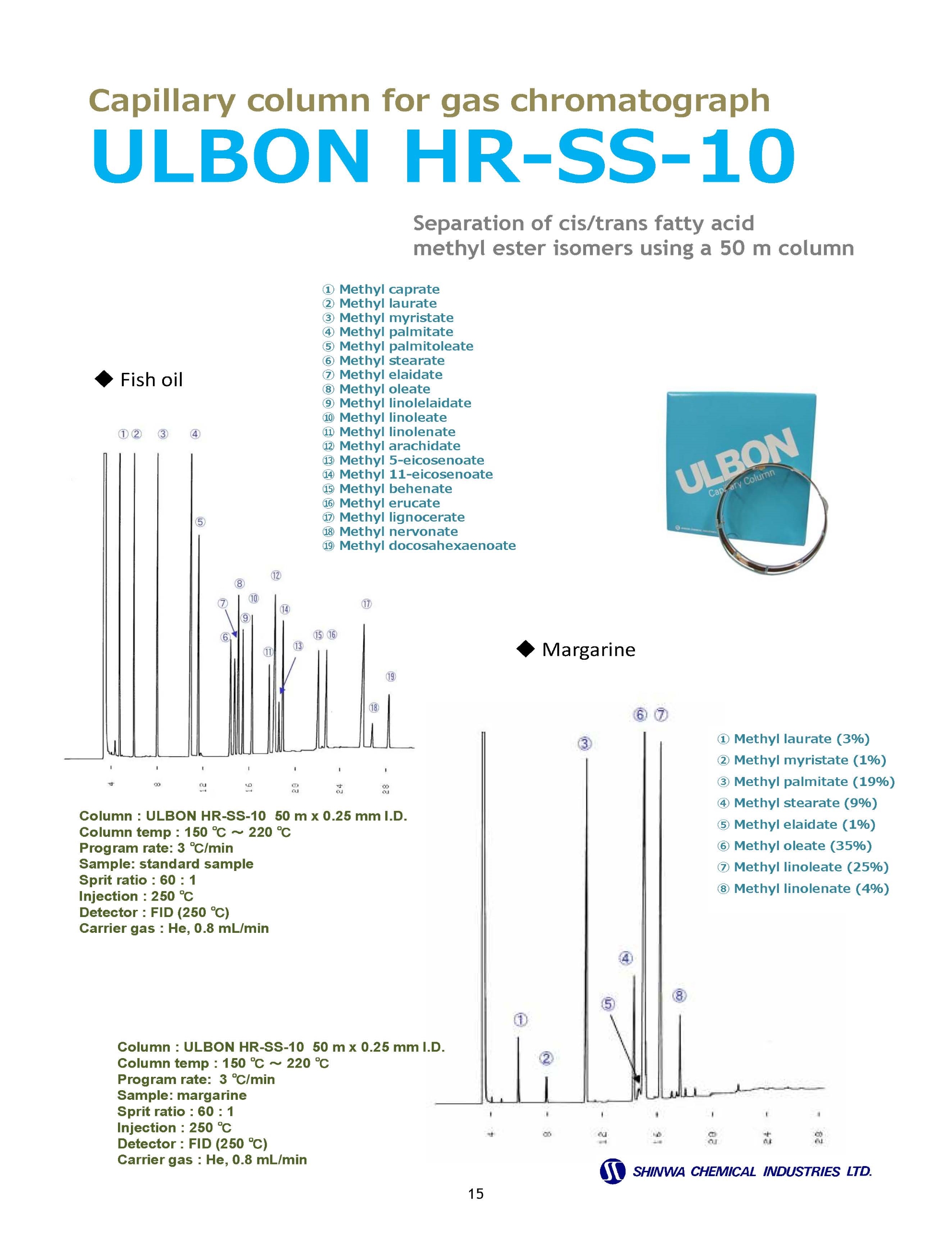
Gas Chromatography Columns
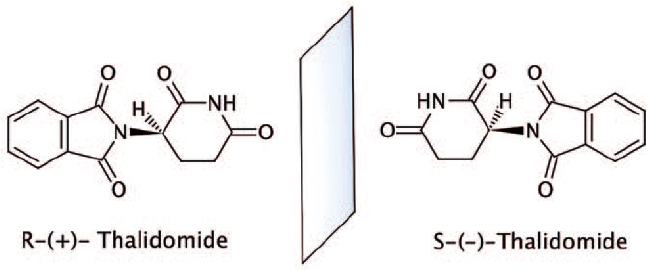
Thalidomide interconverts between (R)- and (S)-enantiomers with protein binding
of 55% and 65%, respectively. The (R)-form is responsible for sedative effects
and the (S)-form is responsible for immunomodulatory effects.
|
Enantiopure drug
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enantiopure_drug
An enantiopure
drug is
a pharmaceutical that is available in one specific enantiomeric form.
Most biological molecules (proteins, sugars, etc.) are present in only one of
many chiral forms,
so different enantiomers of a chiral drug molecule bind differently (or not at
all) to target receptors.
One enantiomer of a drug may have a desired beneficial effect while the other
may cause serious and undesired side effects, or sometimes even beneficial but
entirely different effects.[1] Advances
in industrial chemical processes have made it economical for pharmaceutical
manufacturers to take drugs that were originally marketed as a racemic mixture
and market the individual enantiomers, either by specifically manufacturing the
desired enantiomer or by resolving a racemic mixture.
On a case-by-case basis, the U.S.
Food and Drug
Administration (FDA)
has allowed single enantiomers of certain drugs to be marketed under a different
name than the racemic mixture.[2]Also case-by-case,
the United States Patent Office has granted patents for
single enantiomers of certain drugs. The regulatory review for marketing
approval (safety and efficacy) and for patenting (proprietary rights) is
independent, and differs country by country. |
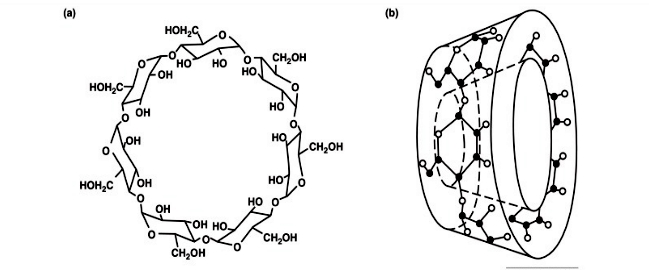
Cyclodextrins
|
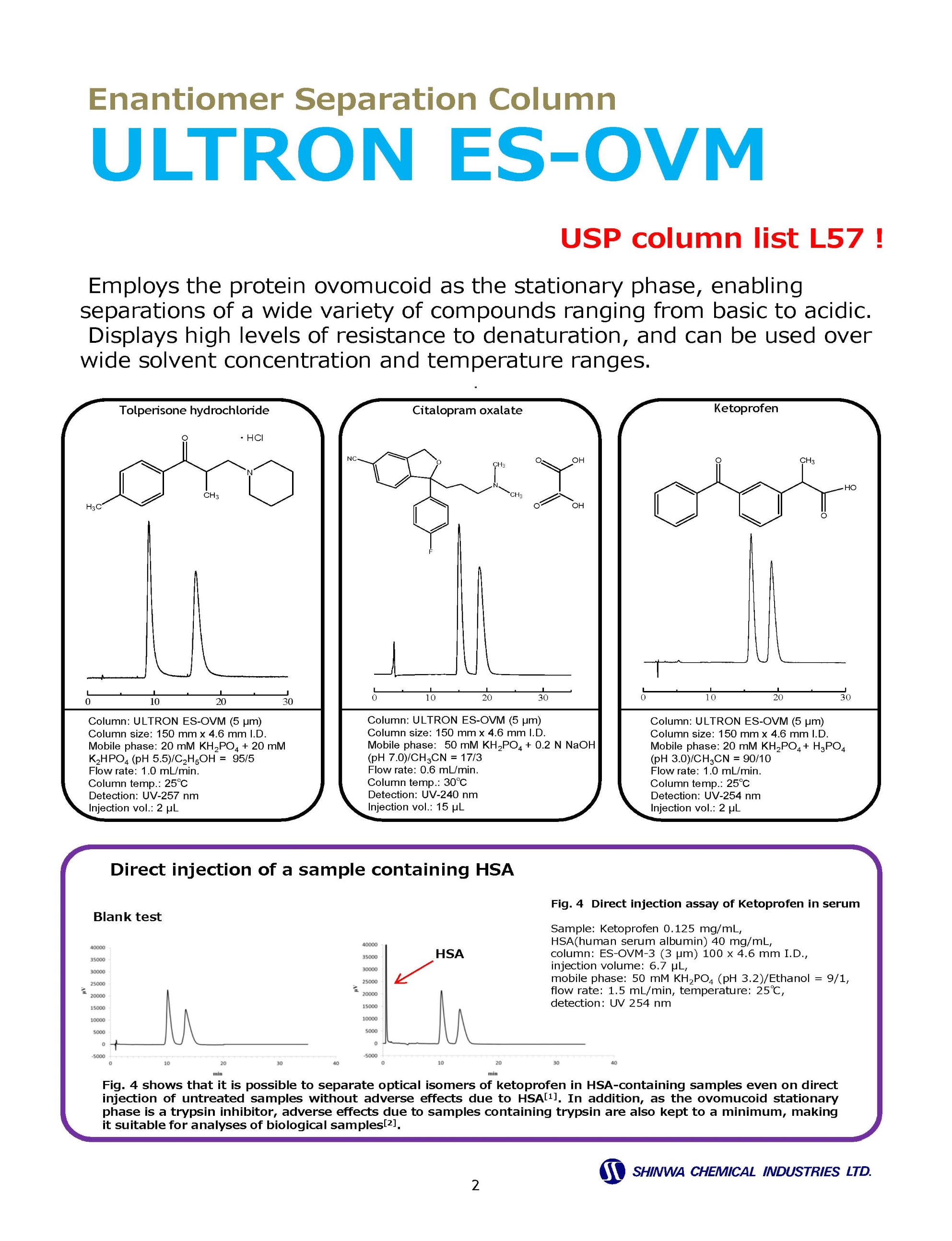
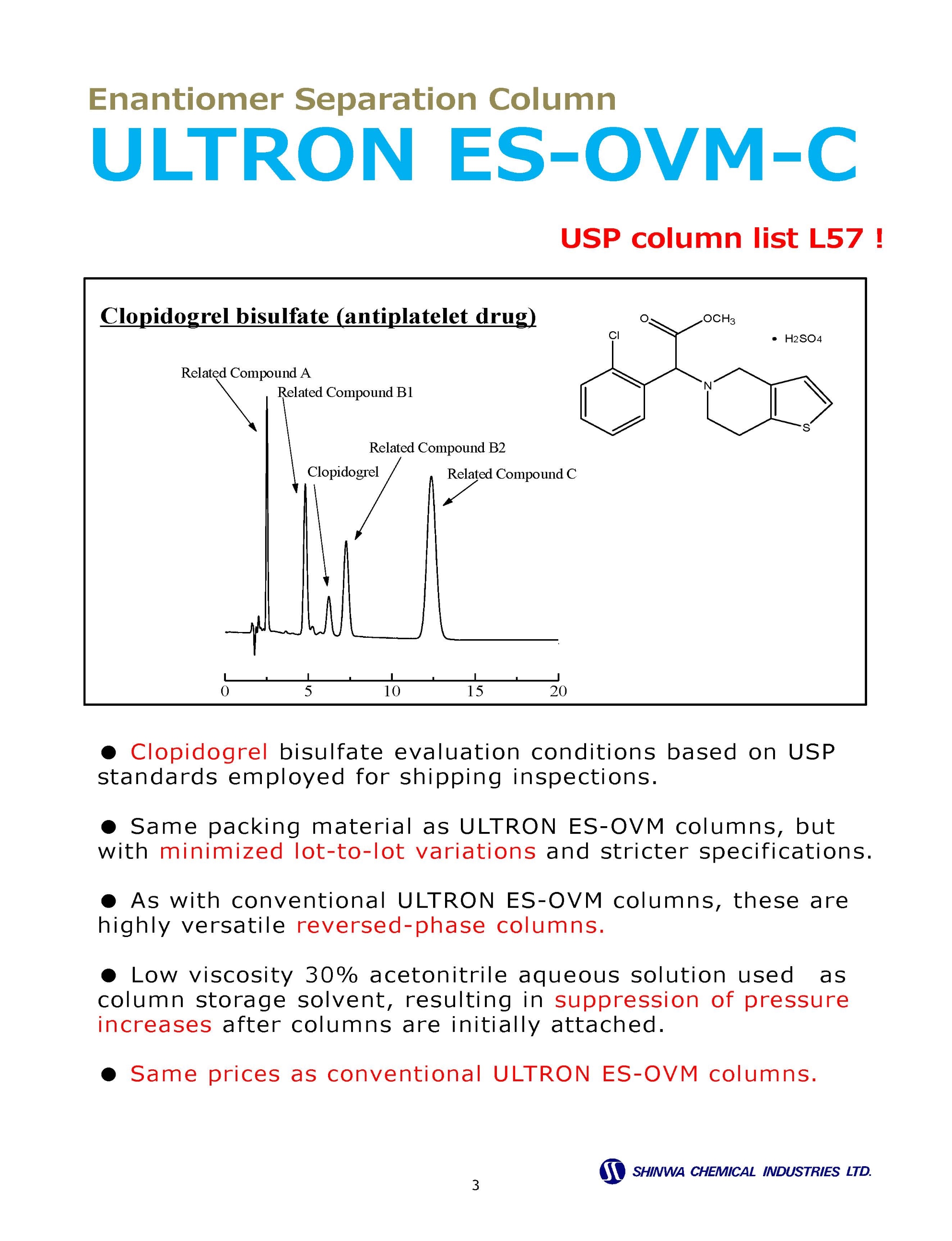
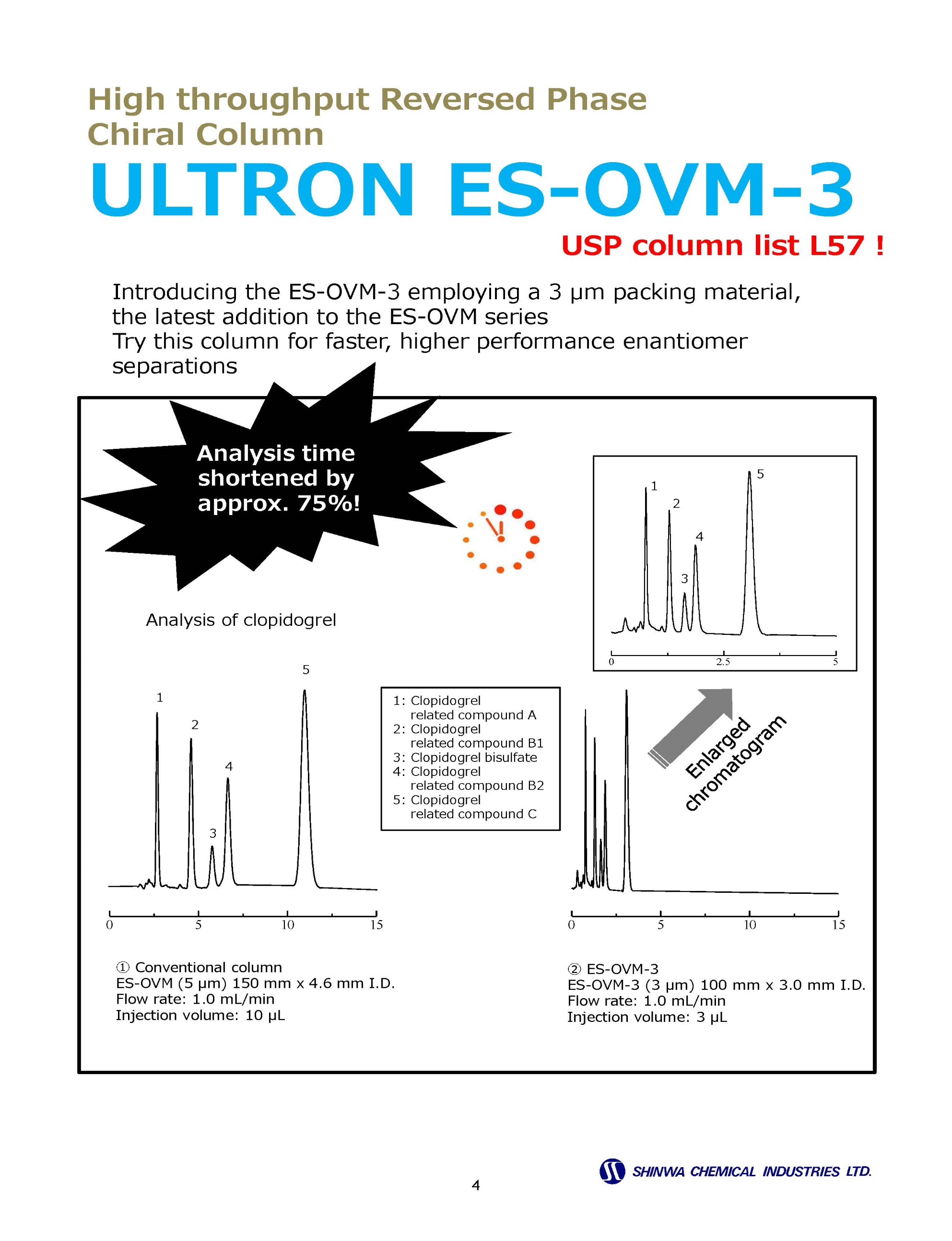
Chiral column chromatography
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chiral_column_chromatography
Chiral column chromatography
is a variant of column
chromatography in which the stationary phase contains
a single enantiomer of a chiral compound rather
than being achiral.
The two enantiomers of the same analyte compound differ in affinity to the single-enantiomer
stationary phase and therefore they exit the column at different times.
The chiral stationary phase can be prepared by attaching a suitable chiral
compound to the surface of an achiral support such as silica gel, which creates a Chiral Stationary Phase
(CSP). Many common chiral stationary phases are based on oligosaccharides such
as cellulose or cyclodextrin(in particular with β-cyclodextrin, a
seven sugar ring molecule). As with all chromatographic methods, various
stationary phases are particularly suited to specific types of analytes.
Chiral Stationary Phases are much more expensive than
comparable achiral stationary phases such asC18.
The principle can be also applied to the fabrication of monolithic HPLC
columns[1] or gas chromatography columns.[2]
|
Leading with Quality, Performance and Cost
Our partners, the Shinwa Chemical Industries are experts in the field of
separation technology.
http://shinwa-cpc.co.jp/en/
Since establishment Shinwa Chemical have especially accumulated a significant
technology and manufacturing know-how through commitment and support for our
customers' research and development requirements with our technology and
experience backed up by a long history. |

|
|
|

|
|






|
|